Hitachi, Ltd and Hitachi Astemo, Ltd. have developed the basic technology for a thin-type inverter that achieves both energy conservation and miniaturization as a power converter (hereinafter referred to as "inverter") for electric vehicles (hereinafter referred to as "EVs").
This technology simplifies power wiring by integrating power semiconductors that control the power supply with printed circuit boards.
Reduced energy loss
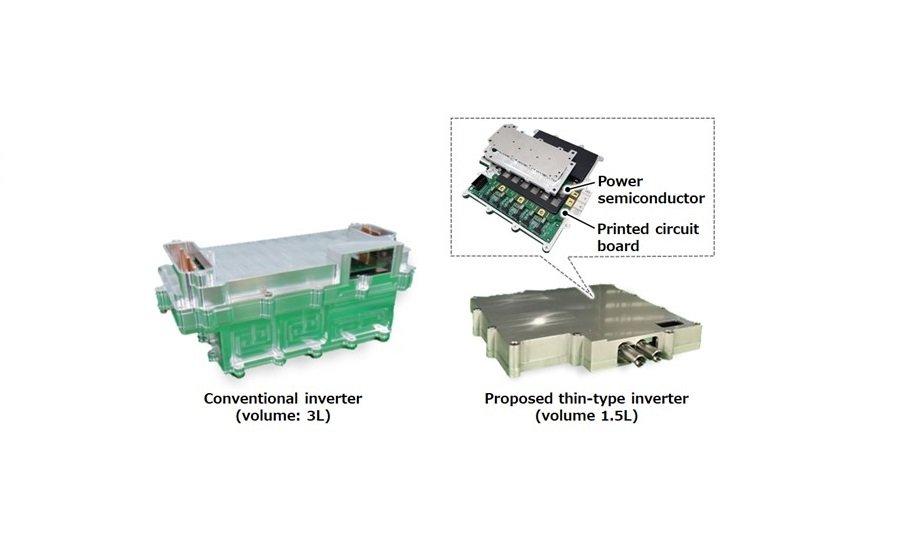
Compared to conventional products, the thin-type inverter reduces energy loss when power semiconductors are switched by 30% and is approximately 50% smaller.
The new design eliminates the need for welding of power semiconductors and power wiring, and the number of components and assembly processes required is also reduced. As a result, throughout the lifecycle of the inverter, including the production process, CO2 emissions are reduced.
Carbon-neutral society
Hitachi and Hitachi Astemo will accelerate efforts to commercialize the thin-type inverter technology
Hitachi and Hitachi Astemo will accelerate efforts to commercialize the thin-type inverter technology, and Hitachi will contribute to the realization of a carbon-neutral society by applying this technology to a wide range of applications, including not only EVs but also EVs fast-charging systems and power transmission systems.
The electrification of automobiles is rapidly advancing as the world aims toward a decarbonized society.
Importance of Inverters
Inverters are an essential component of EVs, converting DC power from the battery to AC power and controlling the rotation of the motor. Inverters are also important components for the effective use of energy, including fast-charging systems for EVs and power transmission systems for renewable energy.
As the introduction of EVs and renewable energy increases in the future, inverters with conventional structures will require larger power semiconductors and peripheral components to control the power supply, which will increase energy loss and complicate the assembly process.
Applications and features of inverter
Hitachi and Hitachi Astemo have been providing inverters for various applications to customers around the world and have now developed the basic technology for a thin-type inverter with a completely different structure. The features are as follows:
1) Technology to integrate power semiconductors and inverter circuit components with printed circuit boards
The entire inverter structure is complex, making it difficult to reduce energy loss, and the size of the inverter
Inverters are composed of power semiconductors that turn large currents on and off, and circuit components that conduct large currents.
Because power semiconductors generate heat when a high current is applied, conventional structures require separate assembly of power semiconductors and inverter circuit components and their connection with wiring. As a result, the entire inverter structure is complex, making it difficult to reduce energy loss and the size of the inverter.
Semiconductor integration
Hitachi and Hitachi Astemo have developed a basic technology that avoids the problem of heat generation by integrating the power semiconductors on a printed wiring substrate that incorporates the inverter circuit components.
This technology simplifies the power wiring inside the inverter and reduces inductance, resulting in a 30% reduction in the energy loss generated when the power semiconductors switch on and off, thus reducing heat generation. The size of the inverter is also successfully reduced by 50% compared to conventional products.
2) Mounting technology to reduce the number of components and processes required for assembly
Conventional inverters use many copper plate components called busbars to supply large currents to power semiconductors, which must be connected by welding or other means.
This required many parts and assembly processes, making it difficult to improve production efficiency.
Reduced energy consumption
The technology reduces energy consumption in the production and contributes to the reduction of CO2
With the mounting technology, power semiconductors and circuit components are mounted on a compact, lightweight, thin printed wiring board, successfully eliminating the need for busbars.
This has greatly simplified the production process, reducing the number of components and assembly steps. The technology reduces energy consumption in the production process and contributes to the reduction of CO2 emissions over the lifecycle of the inverter.
Automotive Engineering Exposition 2022
The developed inverter will be exhibited at the Automotive Engineering Exposition 2022 to be held at Pacifico Yokohama from May 25, 2022.
Main specifications of the thin-type inverter
- Volume: 1.5 L
- Maximum Output: 170 kVA
- Maximum Current: 350 A
- Power Density: 113 kVA/l